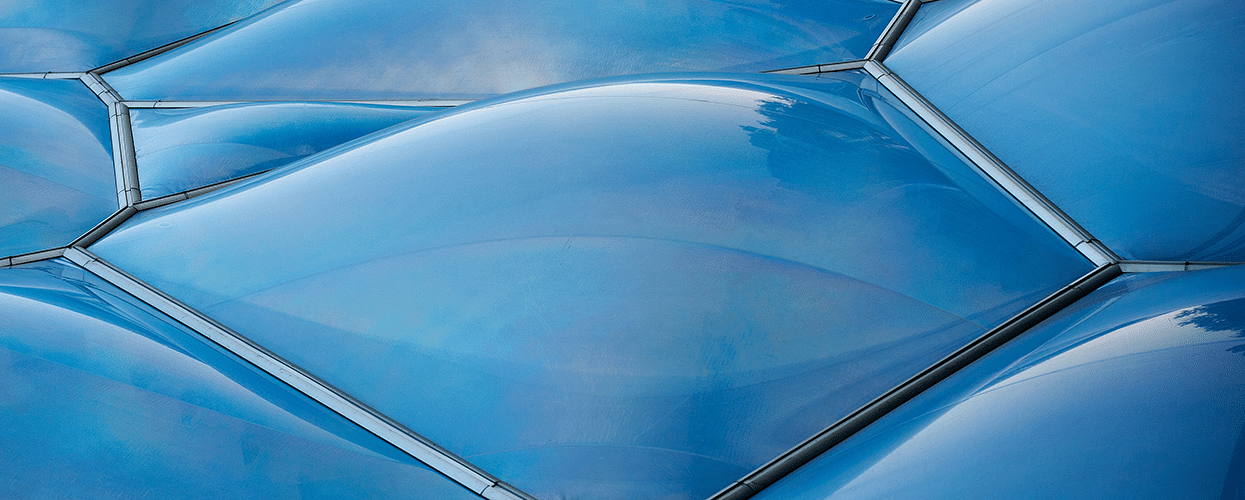
A building envelope has three standard functions: keep cold air out in winter, keep cool air in summer, and meeting the specified U-value requirements. However, not all solutions are created equal, especially when considering the aesthetic appearance of the structure. When the structure needs to be eye-catching, a facade or building envelope comprised of two or more layer ETFE cushions has become established as an attractive, flexible solution.
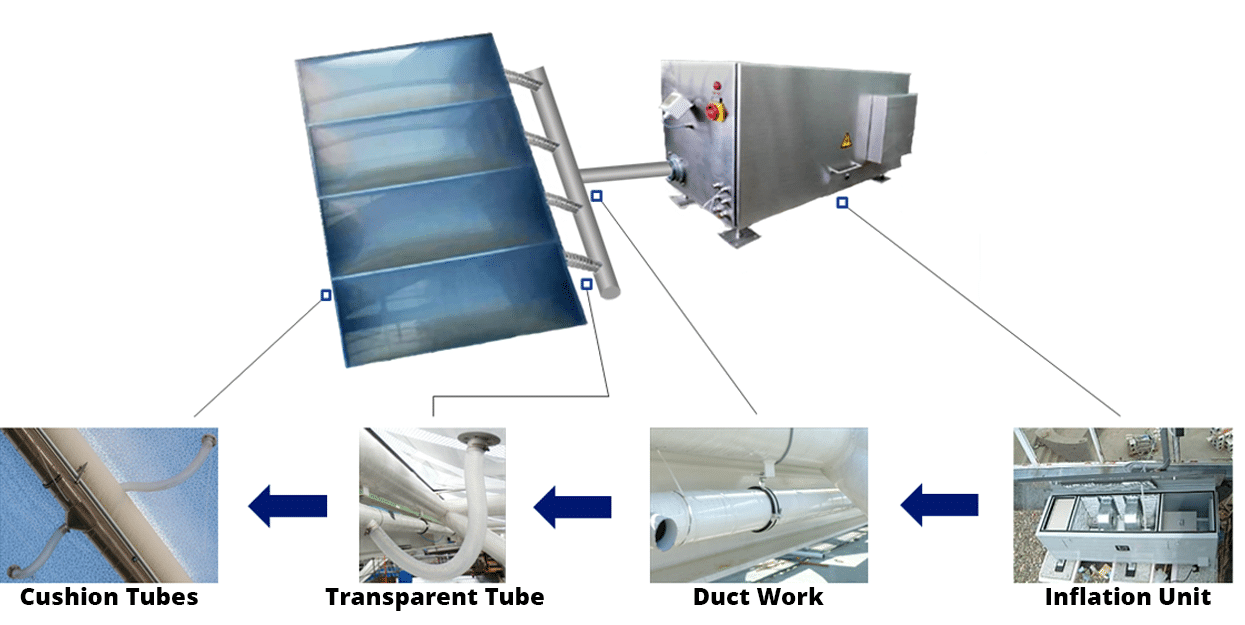
ETFE cushion & aluminum profile
ETFE cushions consist of two or more layers of film that are welded together at the edge. The cushions may vary in shapes and sizes, depending on weather loads (snow, wind, rain) and building geometry. The edge is clamped with a keder, which is a cord welded into a narrow pocket. A multi-part aluminum frame profile makes the connection to the supporting structure. Here, an extruded aluminum profile receives the keder in a groove and is then hooked into a base profile that is connected to the supporting structure. Depending on the profile system, cover profiles or retaining screws ensure a permanent, force-fit connection between the cushion and the supporting structure.
Air supply system
At the edge of each ETFE cushion is an air inlet nozzle connected to a tube system via a flexible hose. A redundant inflation system consisting of main and reserve blowers provides the necessary supporting air. A positive operating pressure of 200 to 600 Pa (4 to 12 psf) inside the cushion is used to support external loads such as wind and snow.
A control system keeps the cushion pressure within the defined limits and switches on the second supply if a blower fails. The system operates with high energy efficiency with a power consumption of about 60 W per 1,000 m² (about 10,000 square feet) of cushion area, and condensation inside the ETFE cushions can be prevented by integrating an air dryer into the inflation unit. Replaceable air filters are used to ensure that the outside air that is taken in by the inflation unit is dust-free.
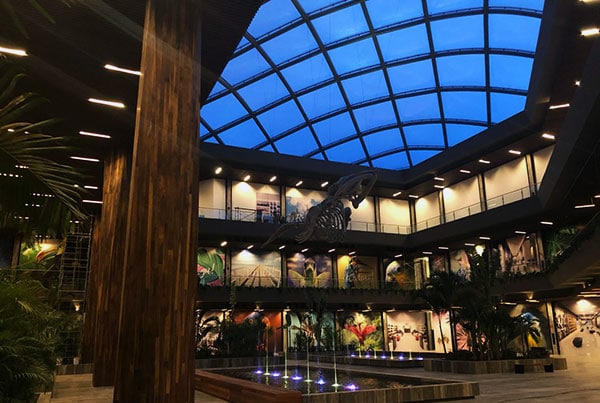
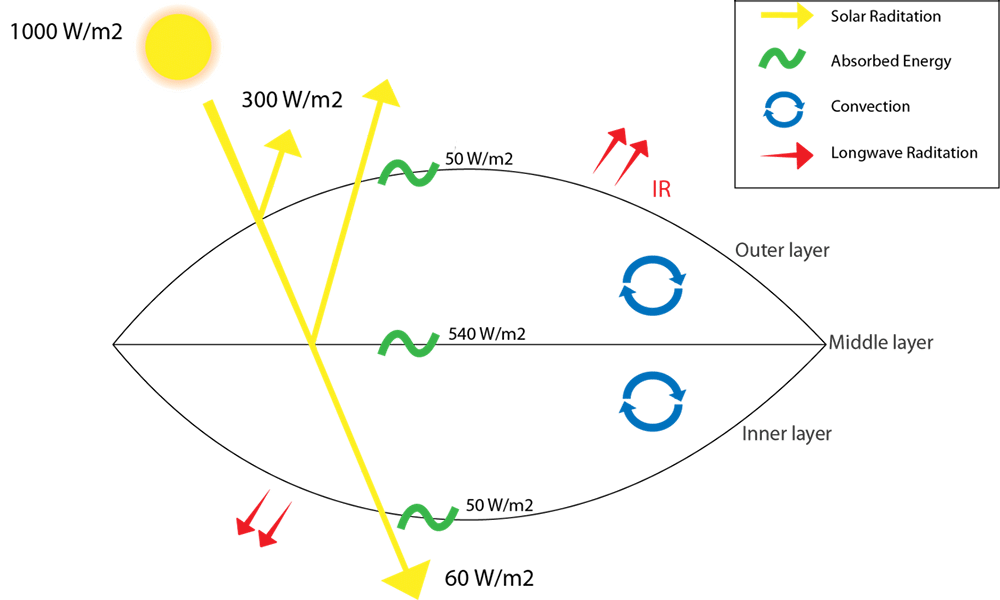
Multilayer cushions as heat and light barrier
Multilayer ETFE cushions allow an energy-efficient system design for closed buildings or enclosures. The ETFE cushion’s thermal resistance results from the number of foil layers separated by air layers.
ETFE cushions have high light and UV transmittance; they are ideal for greenhouses, zoological gardens, or similar facilities. The desired Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) value can be achieved by printing a special reflective ink, known as fritting.
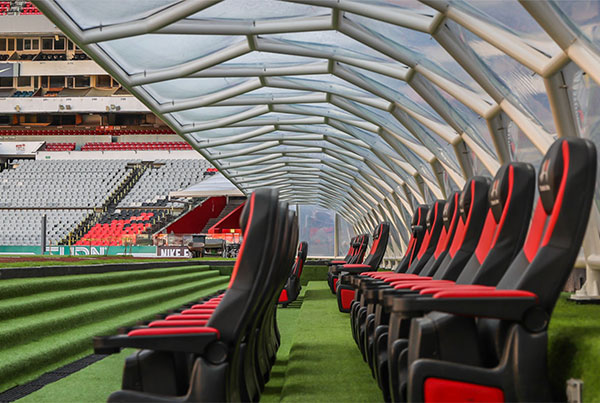
Two-layer cushions as a design element
ETFE cushion systems are an excellent alternative to single-layer ETFE films in enclosures.
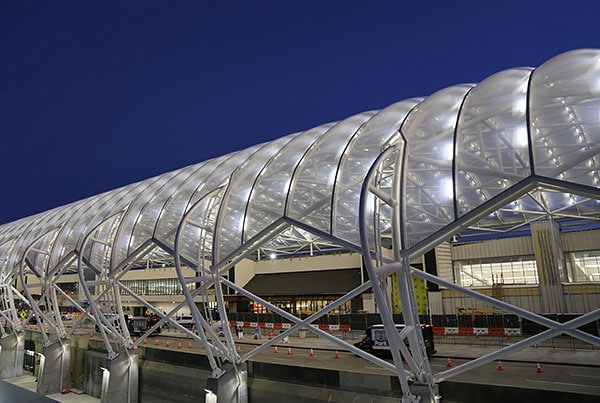
If a roofing structure has a horizontal surface at the top and is sloped at the sides, water ponding conditions must be prevented from forming in the low-sloped areas near the ridge. This can be done with single-layer ETFE by using stronger foil material, which makes the installation more difficult, increasing the slope, adding an array of support cables, and/or other means that reduce the water retention to a minimum.
However, two-layer ETFE cushions can be used without any problems in that sort of geometry while still providing the structure with the unique appearance only ETFE can provide.
Prefabrication makes transportation and installation easy
ETFE cushions, mounting profiles, and fastening elements can be precisely prefabricated according to the factory plan or measurements. The cushions are foldable and thus compact for transportation. The mounting profiles are sent in sections and attached to the supporting structure in-situ, and connection to the air supply as well as functional testing are carried out by experts on site.
ETFE cushions need less cleaning!
The surfaces of the ETFE cushions are very smooth, which prevents most dirt from adhering to the material. When it rains, the surface cleans itself; and in sandy or dusty environments, the low surface energy of the material resists dirt and dust from sticking.








